- SOLUTIONS
-
- Countries
- Stories
- About Us
-
-
- HOW CAN WE HELP?
- Find out how we can assist you to achieve higher growth through services that are tailored to your company needs.
-
- GLOBAL INSIGHTS
Hire Globally
Pay Locally
Expand Quickly



Trusted by 3,200+ Companies
160+ Countries and counting …
Trusted by 3,200+ Companies
160+ Countries and counting …


















today
simple
Select Your Ideal Job Candidate
Initiate INS Global Set-Up & Contract Creation
Onboard through a Globally Compliant Payroll System
Select Your Ideal Job Candidate
Initiate INS Global Set-Up & Contract Creation
Onboard through a Globally Compliant Payroll System
who
Since 2006, INS Global has been building a worldwide community of professionals and industries to connect the right companies to the right talent in the simplest, most efficient, and most compliant way possible
what
When you need support, you will work directly with your assigned advisor, who is an expert in the region you are hiring in

testimonials
Ins Global supports business expansion in Portugal and France, easing global payroll and tax compliance, focusing on business growth.
Lesia P
Company Name
INS Global’s commitment to addressing compensation, harassment, and employment issues promptly lets us focus on core work.
Juan I.
Company Name
INS Global provided an innovative PEO solution, more efficient than traditional global entity setup, enhancing our core focus.
Louis L.
Company Name

features
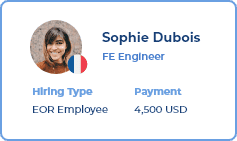
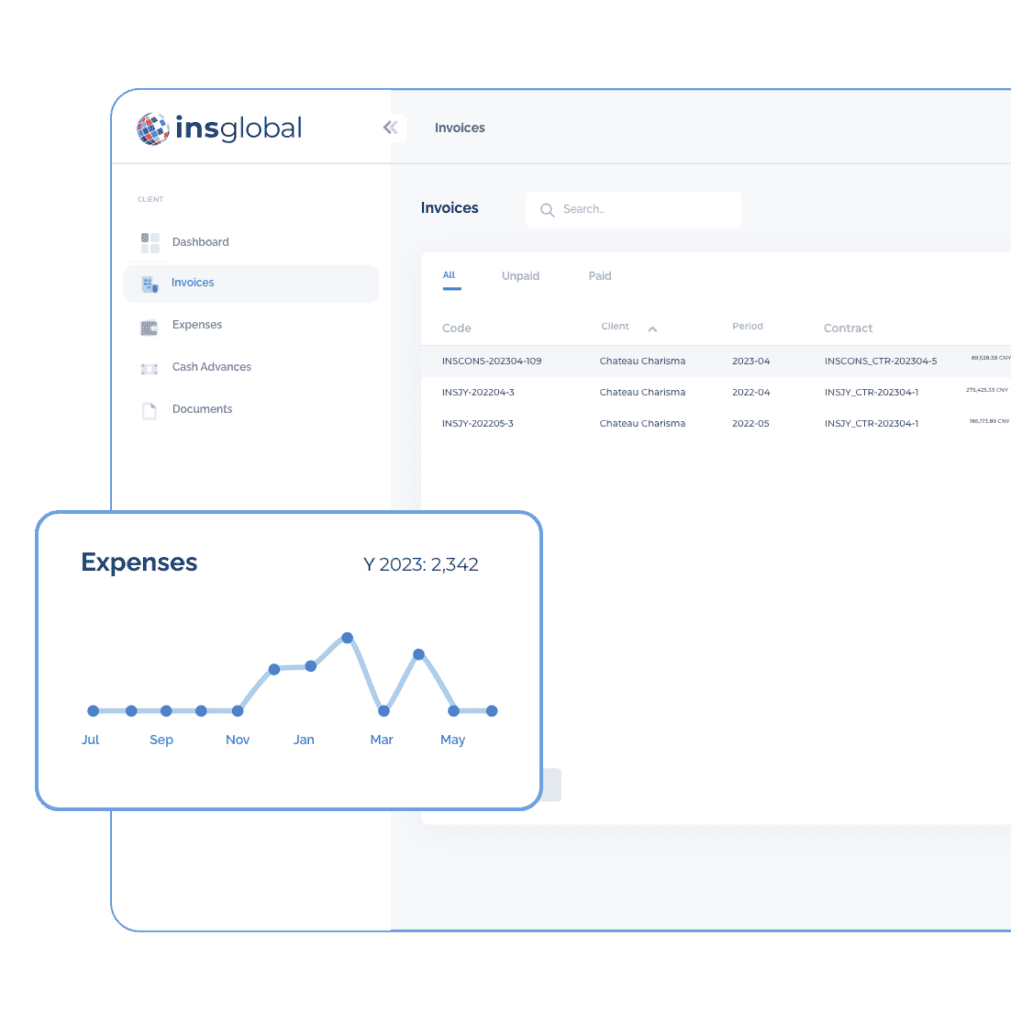
Quickly view and manage invoices, cash advances, and employee expense requests.
Initiate cash advances for flexibility in managing finances.
Allow employees to submit expenses and managers to approve them seamlessly at home and abroad.
Access, review, or download important contracts with ease.
Need assistance? Get in touch instantly with our support teams around the world.
numbers
content