- SOLUTIONS
-
- Countries
- Stories
- About Us
-
-
- HOW CAN WE HELP?
- Find out how we can assist you to achieve higher growth through services that are tailored to your company needs.
-
- GLOBAL INSIGHTS
INS Global is your local provider for consulting and Human Rrsources outsourcing. By using our PEO (Professional Employer Organization) in the Philippines, our staff can help you hire employees and start operating your business quickly, all without the burdensome red tape and the associated costs of global expansion.
Our PEO, sometimes confused with an Employer of Record (EOR), operates in the Philippines as a local partner for companies wishing to expand into this new market without having to establish a separate legal entity.
A PEO in the Philippines as a third-party organization that takes on the responsibilities of an employer, provides crucial HR outsourcing services to companies seeking quick, safe, and cost-effective strategies for global mobility.
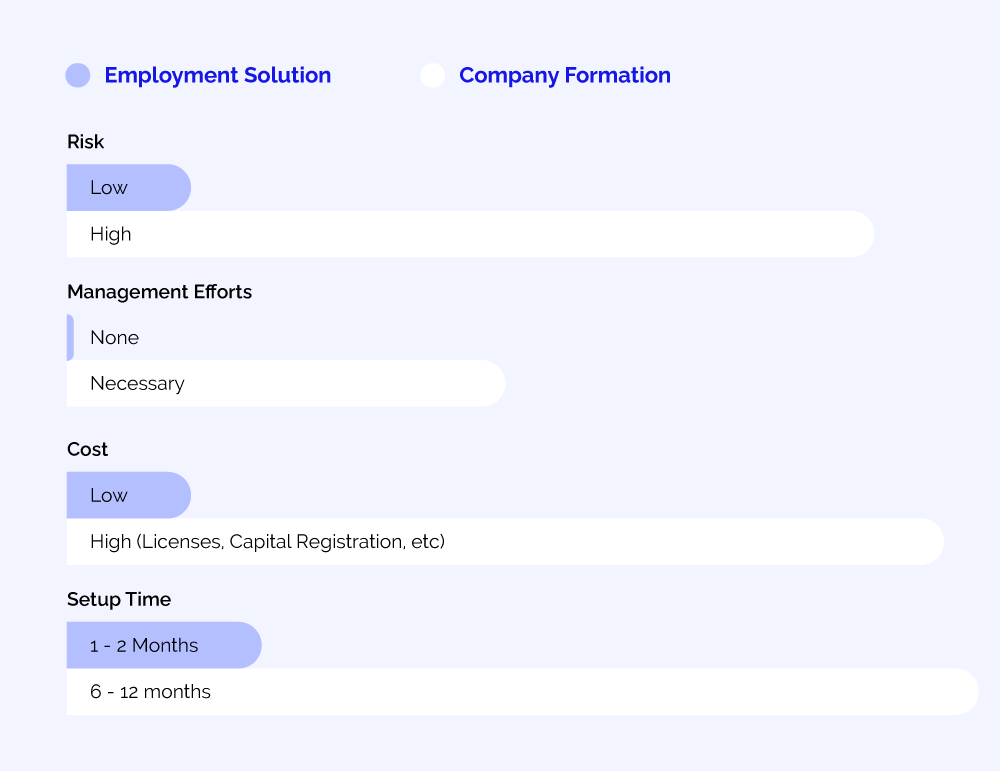
An Employer of Record (EOR) in the Philippines provides companies with a cost-effective and simple solution for the complications of overseas hiring and employee management.
Incorporating a company in the Philippines can be overly complicated and time–consuming, requiring you to understand local laws and to establish a physical presence. PEOs allow you to operate in the Philippines without going through the convoluted, time-consuming steps required to form and incorporate a legal entity.
A PEO:
A PEO offers you extensive knowledge of local regulations and up-to-date best practices for local administrative procedures that will keep your company in legal compliance.
When entering into a new market, like the Philippines, simple mistakes in the HR department can lead to a high occurrence of fees and fines that slow down business. A PEO reduces these risks, increases your market entry time, and saves you money.
PEOs can provide payroll outsourcing in the Philippines, along with recruitment, headhunting, and management services. When your company doesn’t have to waste valuable time on these issues, you can focus on what matters most, company growth.
Estimated time for Company Incorporation in the Philippines: 4-12 months
Estimated time to establish a PEO in the Philippines: 5 days
*Estimate
Everything you need is provided by one point of contact. This decreases the risk of misunderstandings, and provides you with custom-built solutions.
INS Global’s Employer of Record will manage employee recruitment and assignment needs in the Philippines in 4 steps:
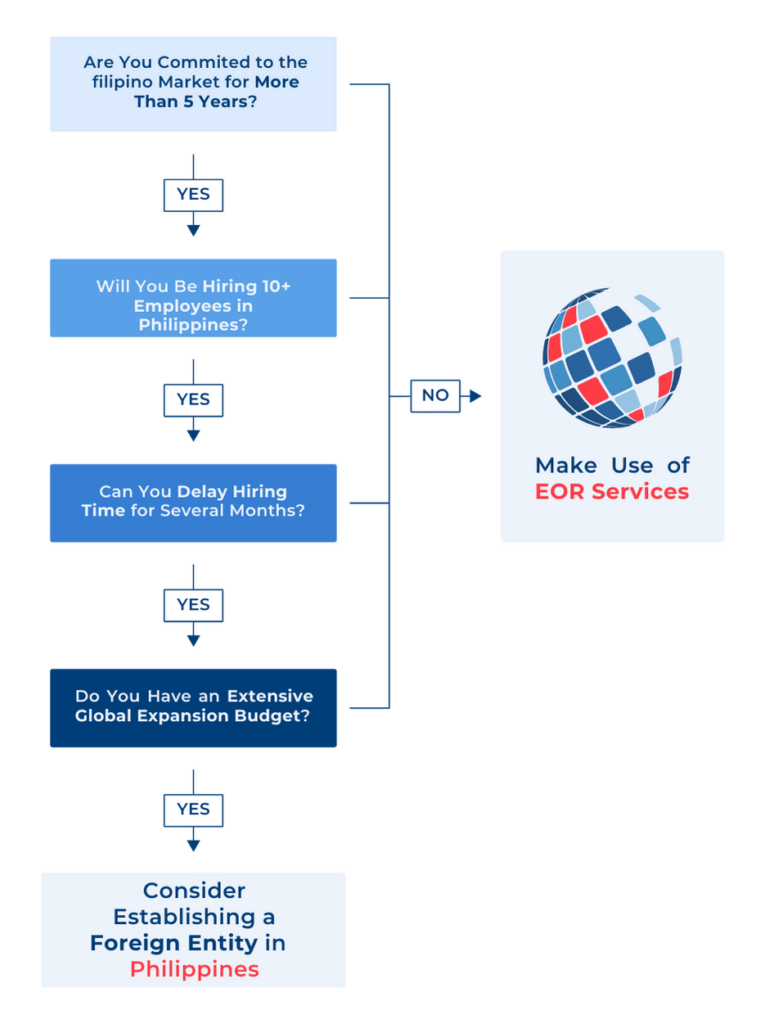
Once you’ve decided to expand and enter the Philippines market, choosing between a PEO and an EOR can be a confusing process. You must be fully informed of their differences to make the best decision for your company.
INS Global offers both PEO and EOR services in the Philippines to best suit your needs.
The main source of employment law in the Philippines is the “Labour Code of the Philippines“. The Constitution provides employers with guidance, while the Philippine Supreme Court supplements this guidance with many employment-related legislations. Additionally, the Department of Labour and Employment (DOLE) provides administrative issuances.
The Labour Code also provides for minimum terms and conditions of employment. Terms can be implied by custom or law, like an employee’s duty to serve their employer with fidelity, honesty, and good faith, and obeying all reasonable dictates from the employer.
Under Article 82 of the Labour Code, working hours apply to all employees, excluding the following:
The normal working hours should not be in excess of 8 hours per day and should exclude the 1-hour daily lunch break. These working hours include all time an employee is required to be on duty, and short rest periods. More info about minimum wage here.
Every employee should be paid a night-work premium that is not less than ten percent of their current wage for each hour of work between 10pm-6am. Work may be performed beyond 8 hours a day if the employee is paid the overtime rate, which is their traditional wages plus 25%. Any work performed during a holiday shall be paid at their regular rate plus 30%.
In the Philippines, holidays include:
Service Incentive Leave (SIL) is the primary leave benefit tha the Labour Code mandates. In accordance with Article 95 of the Labour Code, every employee who has worked for one year shall be entitled to at least five days paid leave. Companies that employ less than 10 people are exempt from this requirement.
As the Labour Code doesn’t explicitly mention vacation leave or sick leave apart from SIL, there is no minimum required amount for these two categories. The total amount of vacation and sick leave are subject to the contract signed between the employee and the employer.
Maternity leave consists of 105 days with full pay, with the option of extending the leave for an additional 30 days without pay. Additionally, single female parents are entitled to an additional 15 days with full pay.
For instances of miscarriage or termination of pregnancy, female employees are entitled to 60 days of leave with full pay. None of these leave days are convertible to cash and are all non-cumulative.
Paternity Leave allowance is 7 days.
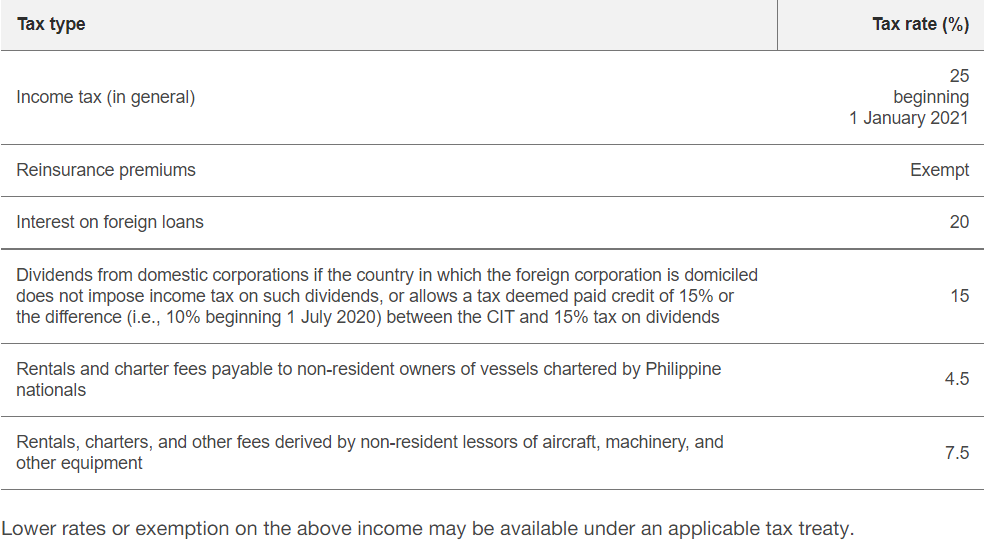
A domestic corporation is subject to tax earned from its worldwide income. In contrast, a foreign corporation is only subject to the taxes that are earned on income from Philippine sources. Resident foreign companies (companies earning money in the Philippines through a branch office) are taxed in the same way as domestic companies, but only on income earned through Philippine–related business.

Non-resident foreign corporations are subject to the following corporate tax rates regarding the gross income derived from operating inside the Philippines.
Working with a reliable PEO in the Philippines to manage all important HR responsibilities, such as payroll, contract administration, and assuring tax compliance, comes at a low cost that is calculated as a monthly charge based on the earnings of the co-employed personnel.
Working with an EOR will allow you to transfer staff to the Philippines securely, efficiently, and legally. This form of outsourcing can be used either temporarily or permanently and offers total compliance assurance as part of the service.
When an employee’s HR needs are managed by a PEO, they have access to several benefits, such as full legal protection, local understanding of all employer responsibilities, timely and accurate payment, improved employee perks, and more.
By maintaining complete control over their work process, contractors who interact with clients through a PEO have access to all the same perks and protections as regular employees.
Indeed, a PEO takes into account any differences in local or regional employment regulations while offering you protection no matter where you are.
In addition to wages and any payments made to recruiting agencies or experts, indirect expenditures such as social insurance contributions, bonuses, or incentives must be included in payroll expenses.
Also, even though signing bonuses are optional, they should be considered when determining recruiting expenditures as they could make you stand out to potential new hires.
With certain PEO organizations, there may be a minimum or maximum number of employees you may hire at one time. Nonetheless, with INS Global you are free to co-employ as many or as few employees as your development strategy requires.
Like many other countries, the Philippines has effectively adapted to the possibility of employee remote work since the COVID-19 outbreak. Companies being opened in the Philippines require proof of address. Employees of a firm with its headquarters in the Philippines should also still have the option between a physical workspace and a home office for fair employment practices and as a competitive incentive.
To assist you in finding the ideal new team member in the Philippines, members of our recruitment team have access to professional networks, knowledge of offline and online business resources, familiarity with local best practices, and more.
INS Global can use our recruitment services to assist you in locating the best talent among both Filipino citizens and foreign residents.
Companies of all sizes, from SMEs to multinational businesses, who are searching for a quick, easy, and secure approach to joining the Philippine market should use a PEO to streamline their expansion strategy.
With our legal experience being ideal for anybody who either lacks their own internal structures or wants to reduce company bloat while expanding, INS Global offers high-quality PEO services to businesses in a wide range of sectors.
Philippine direct hiring of independent contractors is an option, as well as hiring them through an intermediary like a staffing agency or an umbrella company. Via networking, job boards, social media, trade associations, and other means, you can connect with a vast array of contractors.
The majority of the time, an independent contractor can work as a self-employed freelancer or through their own limited liability company or sole proprietorship, through which they can issue bills to clients.
Contractor work agreements should be carefully worded to avoid any kind of misclassification.
Employees are typically paid monthly, with tax and social security deductions being made by employers at the source. The country has a mandatory requirement for companies to make a 13th–month payment at the end of every year.
The minimum wage in the Philippines is determined by each region individually. A list of the minimum wage per region can be found here.
All workers moving to the Philippines or living in the Philippines for purposes of employment must apply for a work permit and an Alien Employment Permit (AEP). These can be applied for after the worker has entered the country on a tourist visa.
Along with individual income taxes, employee payroll in the Philippines includes several deductions for social security, health insurance, and the Home Development mutual fund. These contributions are shared between the employee and employer, with the employer expected to match the employee’s contributions up to a maximum of PHP 35,400 per year.
Additionally, employers must make contributions to the Employee’s Compensation Fund each month.
Employees in the Philippines are entitled to a range of benefits, including healthcare, unemployment insurance, and several forms of paid leave, all of which are paid for by social security contributions.
Although verbal agreements are permitted in the Philippines, employers cannot modify an employment contract without the employee’s approval. It’s considered best practice to have this approval in writing. Changes in this situation must nonetheless abide by the minimum requirements of the law.
The Philippine national health service (PhilHealth) provides free healthcare to all employees (whether local or foreign) who are enrolled in the national health insurance program. Companies and employees may also choose to seek private healthcare through private health insurance available throughout the country.
Severance pay, called separation pay in the Philippines, should be provided in a limited number of circumstances (typically where termination occurs through no fault of the employee. This pay amounts to one month’s pay per year of service.
The Department of Labor and Employment (DOLE) serves as the main administrative body for labor and employment regulations. It is primarily responsible for improving worker welfare, and fostering stable working relationships.
There are 10 fully-paid annual national public holidays in the Philippines plus a variable number of special non-working days where payment is not expected.
Level 39, Marina Bay
Financial Centre Tower 2,
10 Marina Boulevard
Singapore 018983